This is the legacy 4D documentation web site. Documentations are progressively being moved to developer.4d.com
 Encrypt page
Encrypt page
You can use this page to encrypt or decrypt (i.e. remove encryption from) the data file, according to the Encryptable attribute status defined for each table in the database. For detailed information about data encryption in 4D, please refer to the Encrypting data section.
A new folder is created each time you perform an encryption/decryption operation. It is named "Replaced Files (Encrypting) <yyyy-mm-dd hh-mm-ss>" or "Replaced Files (Decrypting) <yyyy-mm-dd hh-mm-ss>".
Note: Encryption is only available in maintenance mode. If you attempt to carry out this operation in standard mode, a warning dialog will inform you that the database will be closed and restarted in maintenance mode
Warning:
- Encrypting a database is a lengthy operation. It displays a progress indicator (which could be interrupted by the user). Note also that a database encryption operation always includes a compacting step.
- Each encryption operation produces a copy of the data file, which increases the size of the application folder. It is important to take this into account (especially in macOS where 4D applications appear as packages) so that the size of the application does not increase excessively. Manually moving or removing the copies of the original file inside the package can be useful in order to minimize the package size.
Encrypting your data for the first time using the MSC requires the following steps:
- In the Structure editor, check the Encryptable attribute for each table whose data you want to encrypt. See the Table properties section.
- Open the Encrypt page of the MSC.
If you open the page without setting any tables as Encryptable, the following message is displayed in the page: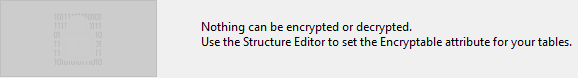
Otherwise, the following message is displayed: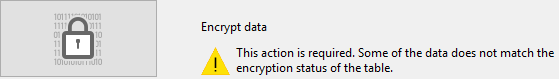
This means that the Encryptable status for at least one table has been modified and the data file still has not been encrypted.
Note: The same message is displayed when the Encryptable status has been modified in an already encrypted data file or after the data file has been decrypted (see below). - Click on the Encrypt picture button.

You will be prompted to enter a passphrase for your data file: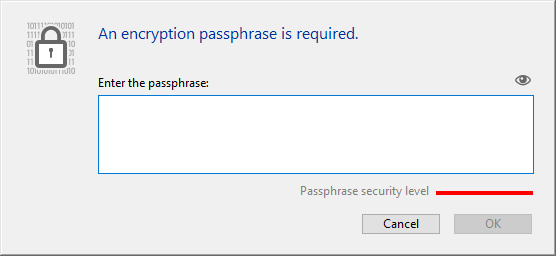
The passphrase is used to generate the data encryption key. A passphrase is a more secure version of a password and can contain a large number of characters. For example, you could enter a passphrases such as "We all came out to Montreux" or "My 1st Great Passphrase!!"
The security level indicator can help you evaluate the strength of your passphrase:
(deep green is the highest level) - Enter to confirm your secured passphrase.
The encrypting process is then launched. If the MSC was opened in standard mode, the database is reopened in maintenance mode.
4D offers to save the encryption key (see Saving the encryption key paragraph below). You can do it at this moment or later. You can also open the encryption log file.
If the encryption process is successful, the Encrypt page displays Encryption maintenance operations buttons.
Warning: During the encryption operation, 4D creates a new, empty data file and fills it with data from the original data file. Records belonging to "encryptable" tables are encrypted then copied, other records are only copied (a compacting operation is also executed). If the operation is successful, the original data file is moved to a "Replaced Files (Encrypting)" folder. If you intend to deliver an encrypted data file, make sure to move/remove any unencrypted data file from the database folder beforehand.
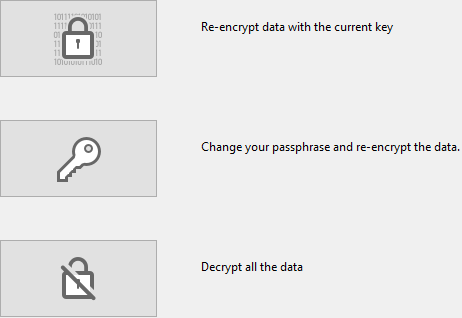
When a database is encrypted (see above), the Encrypt page provides several encryption maintenance operations, corresponding to standard scenarios.
For security reasons, all encryption maintenance operations require that the current data encryption key be provided.
- If the data encryption key is already loaded in the 4D keychain(*), it is automatically reused by 4D.
- If the data encryption key is not found, you must provide it. The following dialog is displayed:
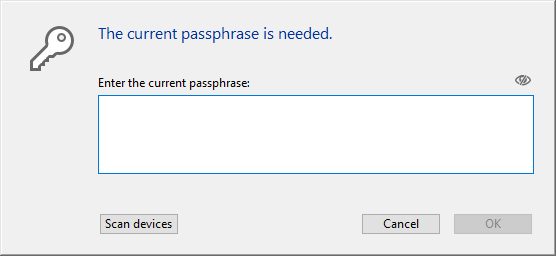
At this step, you have two options:
- enter the current passphrase(**) and click OK.
OR - connect a device such as a USB key (see Storing data encryption keys in files) and click the Scan devices button.
- enter the current passphrase(**) and click OK.
(*) The 4D keychain stores all valid data encrpytion keys entered during the application session.
(**) The current passphrase is the passphrase used to generate the current encryption key.
For more information, please refer to the Concepts and terminology paragraph.
In all cases, if valid information is provided, 4D restarts in maintenance mode (if not already the case) and executes the operation.
This operation is useful when the Encryptable attribute has been modified for one or more tables containing data. In this case, to prevent inconsistencies in the data file, 4D disallows any write access to the records of the tables in the application. Re-encrypting data is then necessary to restore a valid encryption status.
- Click on Re-encrypt data with the current encryption key.
- Enter the current data encryption key (see Providing the current data encryption key).
The data file is properly re-encrypted with the current key and a confirmation message is displayed: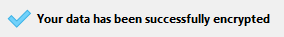
This operation is useful when you need to change the current encryption data key. For example, you may need to do so to comply with security rules (such as requiring changing the passphrase every three months).
- Click on Change your passphrase and re-encrypt data.
- Enter the current data encryption key (see Providing the current data encryption key).
- Enter the new passphrase (for added security, you are prompted to enter it twice):

The data file is encrypted with the new key and a confirmation message is displayed.
This operation removes all encryption from the data file. If you no longer want to have your data encrypted:
- Click on Decrypt all data.
- Enter the current data encryption key (see Providing the current data encryption key).
The data file is fully decrypted and a confirmation message is displayed: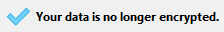
Note: This operation modifies the Encryptable status of your tables. Once the data file is decrypted, the encryption status of tables do not match their Encryptable attributes. To restore a matching status, you must deselect all Encryptable attributes at the database structure level.
4D allows you to save the data encryption key in a dedicated file. Storing this file on an external device such a USB key will facilitate the use of an encrypted database, since the user would only need to connect the device to provide the key before opening the database in order to access encrypted data. For more information, refer to the Storing data encryption keys in files paragraph.
You can save the encryption key each time a new passphrase has been provided:
- when the database is encrypted for the first time,
- when the database is re-encrypted with a new passphrase.
Note: Successive encryption keys can be stored on the same device.
After an encryption operation has been completed, 4D generates a file in the Logs folder of the database. It is created in XML format and named "<DatabaseName>_Encrypt_Log_<yyyy-mm-dd hh-mm-ss>.xml" or "<DatabaseName>_Decrypt_Log_<yyyy-mm-dd hh-mm-ss>.xml".
An Open log file button is displayed on the MSC page each time a new log file has been generated.
The log file lists all internal operations executed pertaining to the encryption/decryption process, as well as errors (if any).
A deeper look into 4D data encryption (blog post)
Encrypting data
Product: 4D
Theme: Maintenance and security center
Created: 4D v17 R5
4D Design Reference ( 4D v21)









