This is the legacy 4D documentation web site. Documentations are progressively being moved to developer.4d.com
- 4D Design Reference
-
- List boxes
-
-
 Overview
Overview
-
 List box specific properties
List box specific properties
-
 List box column specific properties
List box column specific properties
-
 List box header specific properties
List box header specific properties
-
 List box footer specific properties
List box footer specific properties
-
 Using object arrays in columns
Using object arrays in columns
-
 Hierarchical list boxes
Hierarchical list boxes
-
 Using standard actions
Using standard actions
-
 Display of fields in list boxes
Display of fields in list boxes
-
 Displaying the result of an SQL query in a list box
Displaying the result of an SQL query in a list box
-
 Overview
Overview
List boxes are complex active objects that allow displaying and entering data as synchronized columns. They have the same basic features as “grouped scrollable areas,” as well as new expanded possibilities (value entry, column sorting, customized appearance, moving of columns, etc.). A list box type object can be completely set using the 4D Form editor and can also be handled programmatically.
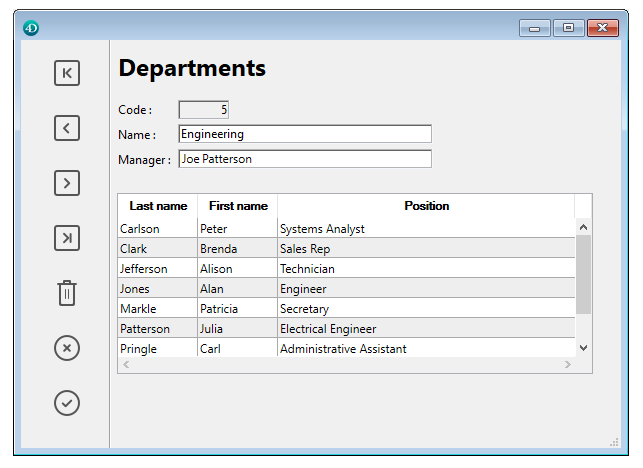
This chapter details the principles related to the creation and configuration of list box type objects in the Form editor. For more information on the programmed management of these objects, refer to List Box of the 4D Language Reference manual.
There are several types of list boxes: selection type list boxes, array type list boxes, and collection or entity selection type list boxes.
- Selection type list boxes: The number of rows is based on the current selection or on a named selection. Each column is associated with a field (for example [Employees]LastName) or a 4D expression. The expression can be based on one or more fields (for example, [Employees]FirstName+“ ”[Employees]LastName) or it may simply be a formula (for example String(Milliseconds)). The expression can also be a project method, a variable or an array item.
In the case of a list box based on the current selection, any modification done from the database side is automatically reflected in the list box, and vice versa. The current selection is therefore always the same in both places. - Array type list boxes: The number of rows is based on the number of array elements. Each column of the list box is associated with a 4D array. By default, 4D assigns the name “ColumnX” to each column variable, and thus to each associated array. You can change it in the column properties. With this type of list box, the values entered or displayed are managed using the 4D language. You can also associate a choice list with a column in order to control data entry (see List box column specific properties).
- Collection or Entity selection type list boxes: The number of rows is based on the number of collection elements or entities. In the column properties, each column is associated with a 4D expression that usually refers to a property path (see List box column specific properties). Collection elements or entities are returned by using the This command (for example, This.firstName to display the value of the "firstName" property/attribute for each element/entity).
Note: Collections and entity selections are very similar when used as list box sources. However, entity selection list boxes benefit from additional features related to user data entry (see Managing entry) since rows are directly connected to data from the datastore.
It is not possible to combine different list box types in the same list box object.
A list box contains one or more columns whose contents are automatically synchronized. By default, when you create a list box, it contains a single column. You can modify the number of columns (add, duplicate, or delete a column) using the context menu (click on a column or column header) or in the list box properties.
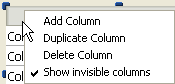
The number of columns is, in theory, unlimited (it depends on the machine resources).
A list box is composed of four distinct parts: the list box object in its entirety, columns, column headers and column footers. In the Form editor, these parts can also be selected separately. Each part has its own name as well as specific properties. For example, the number of columns or the alternating color of each row is set in the list box object properties, the width of each column is set in the column properties, and the font of the header is set in the header properties.
You can display an array type list box either in standard mode or in hierarchical mode. List boxes displayed in hierarchical mode use specific mechanisms that are described below.
During execution, list boxes allow displaying and entering data as lists.
To make a cell editable (if entry is allowed for the column), simply click twice on the value that it contains:
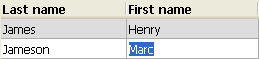
Note: For more information, refer to Managing entry in the 4D Language Reference manual.
You can enter and display the text on several lines within a list box cell. To add a line return:
- Windows - press Ctrl+Carriage return
- macOS - press Option+Carriage return.
Note that the height of the rows is only resized automatically for array type list boxes if the Automatic Row Height option is selected. This option is ignored for selection and collection type list boxes.
It is possible to sort column values by clicking on a header (standard sort). The sort is alphanumerical and alternately ascending/descending on multiple clicks. All columns are automatically synchronized.
Note: For more information, refer to Managing sorts in the 4D Language Reference manual.
It is also possible to resize each column:

The user can modify the order of columns and (array list boxes only) rows by moving them using the mouse, if this action is authorized:
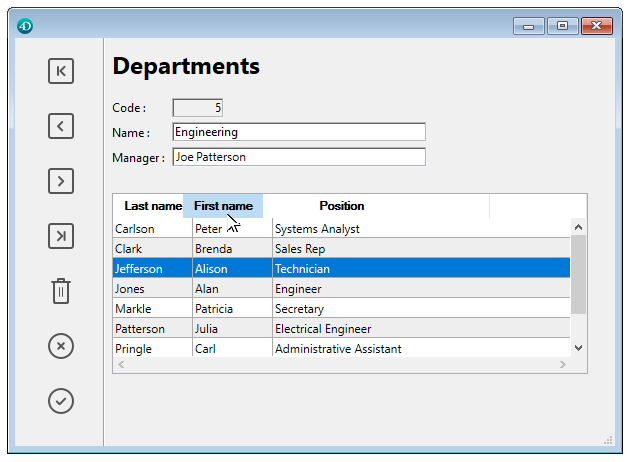
Finally, the user can select one or more rows using the standard shortcuts: Shift+click for an adjacent selection and Ctrl+click (Windows) or Command+click (Mac OS) for a non-adjacent selection.
All these characteristics can be handled using the list box, column, header and footer properties. They are detailed in the following sections.
Note: The specific characteristics of list boxes used in hierarchical mode are described in Hierarchical list boxes.
List boxes can be printed in forms in "preview" mode (printing a picture of the list box area) or in "advanced" mode (dynamic printing in variable size). For more information, refer to Printing list boxes in the 4D Language Reference manual.
Product: 4D
Theme: List boxes
Modified: 4D v17
4D Design Reference ( 4D v20 R7)









